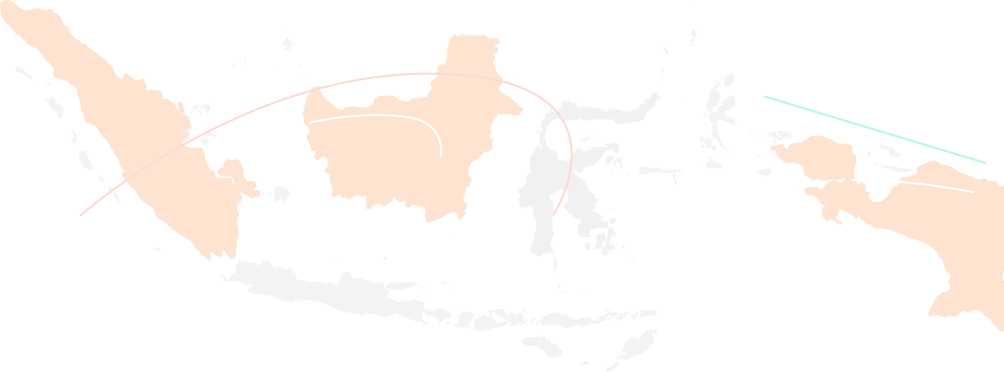
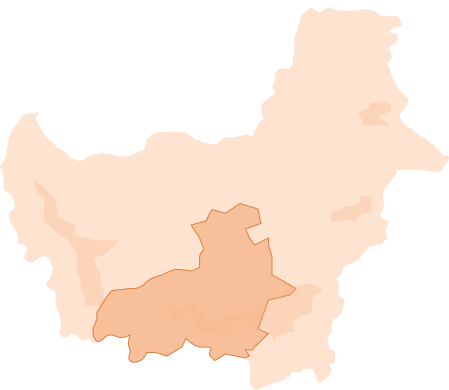
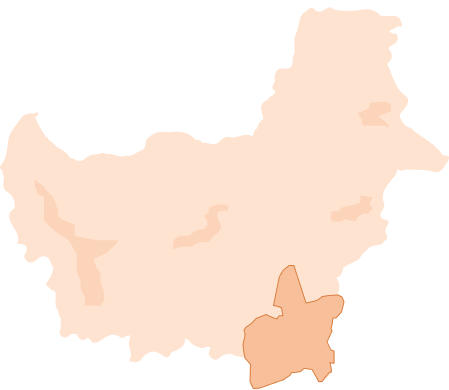
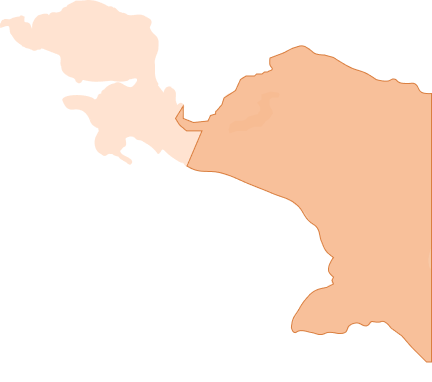
Peatlands on the map
As the proverb goes, what you don’t know, you won’t love. Now, let’s get to know peatlands. Where are the peatlands of Indonesia? How big and how deep are peatlands in various provinces in Indonesia? What is the Peat Ecosystem Function (FEG) and how does it relate to conservation activities?
This menu will outline the answers to these questions. Let’s dive in.
 Overview
Overview
 Threats
Threats
 Potential
Potential